UnifyApps enables seamless integration with MySQL databases as a source for your data pipelines. This article covers essential configuration elements and best practices for connecting to MySQL sources.
Overview
MySQL is widely used for web applications, online transaction processing, and e-commerce platforms. UnifyApps provides native connectivity to extract data from these MySQL environments efficiently and securely.
Connection Configuration

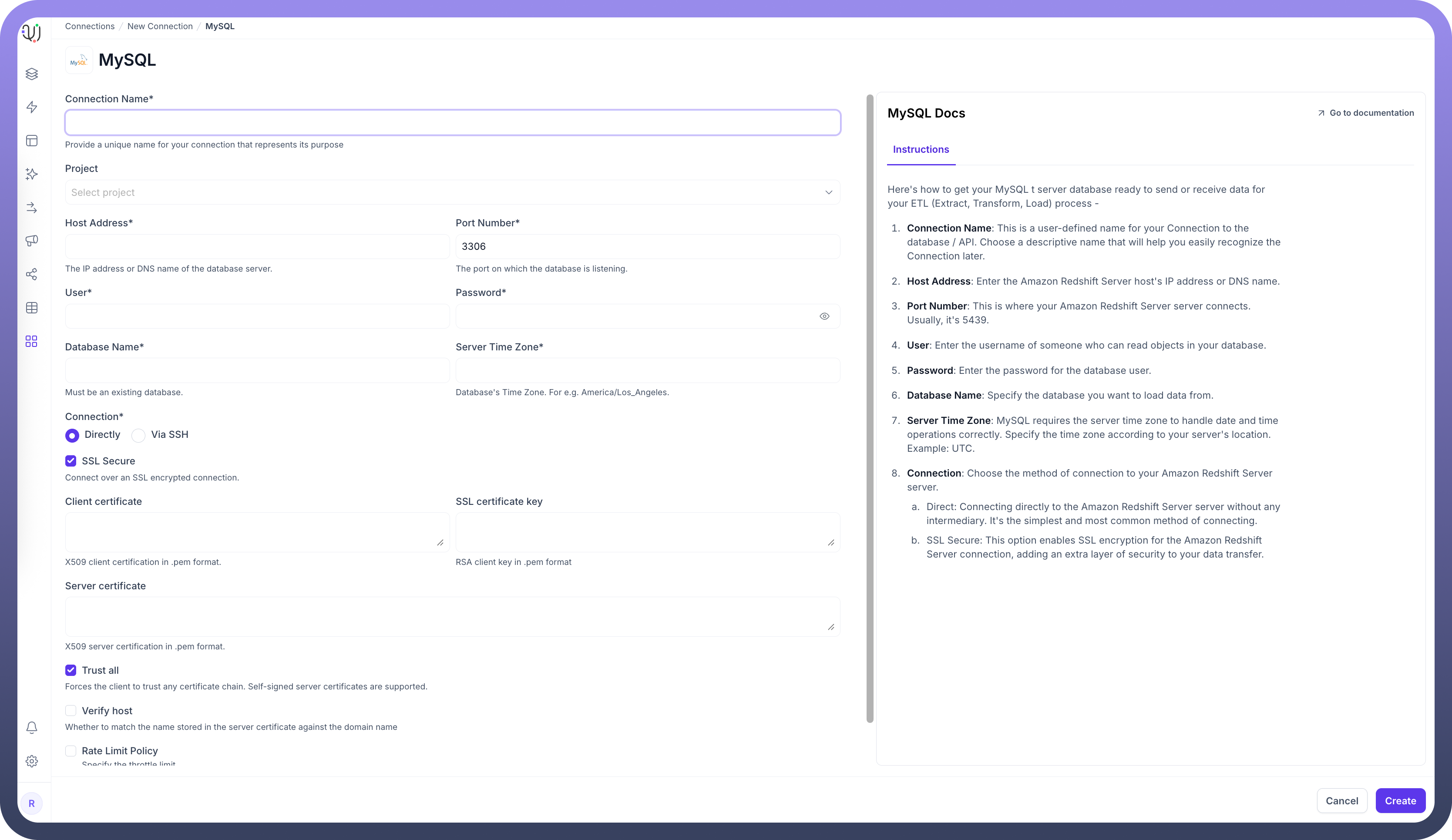
| Parameter | Description | Example |
Connection Name* | Descriptive identifier for your connection | "Production MySQL Web App" |
Project | Optional project categorization | "E-commerce Platform" |
Host Address* | MySQL server hostname or IP address | "mysql.example.com" |
Port Number* | Database listener port | 3306 (default) |
User* | Database username with read permissions | "unify_reader" |
Password* | Authentication credentials | "********" |
Database Name* | Name of your MySQL database | "ecommerce_db" |
Server Time Zone* | Database server's timezone | "UTC" |
Connection* | Method of connecting to the database | Direct or Via SSH |
To set up a MySQL source, navigate to the Connections section, click New Connection, and select MySQL. Fill in the parameters above based on your MySQL environment details.
Server Timezone Configuration

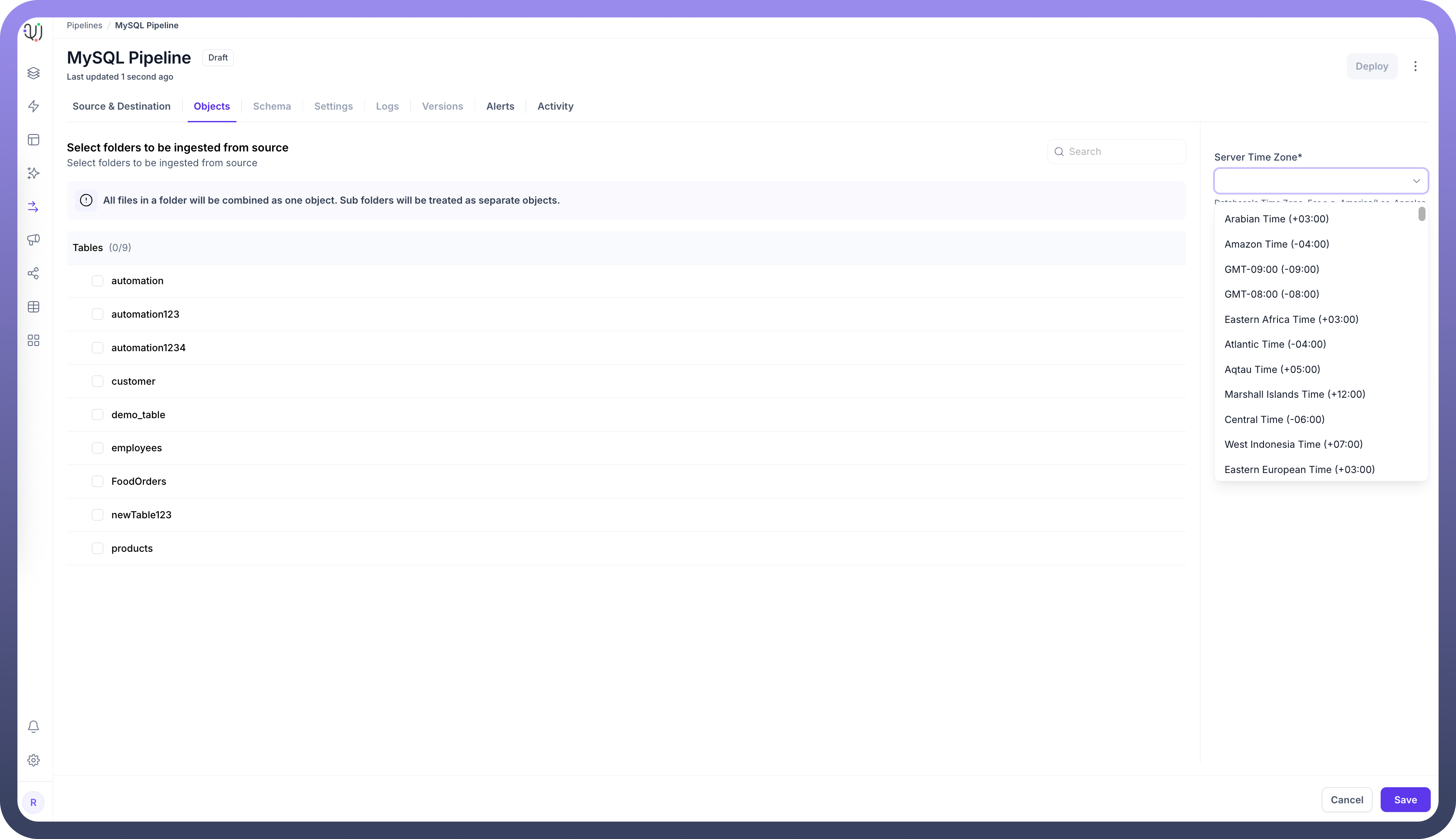
When adding objects from a MySQL source, you'll need to specify the database server's timezone. This setting is crucial for proper handling of date and time values.
In the Add Objects dialog, find the Server Time Zone setting
Select your MySQL server's timezone
This ensures all timestamp data is normalized to UTC during processing, maintaining consistency across your data pipeline.
Ingestion Modes
| Mode | Description | Business Use Case |
Historical and Live | Loads all existing data and captures ongoing changes | E-commerce platform migration with continuous order synchronization |
Live Only | Captures only new data from deployment forward | Real-time inventory tracking without historical data |
Historical Only | One-time load of all existing data | Marketing analysis or quarterly reporting snapshot |
Choose the mode that aligns with your business requirements during pipeline configuration.
Binary Log Configuration for Change Data Capture
For Historical and Live or Live Only modes that track ongoing changes, MySQL's binary logging must be properly configured:
Server Configuration: Edit your MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini) to enable binary logging:
[mysqld] server-id=1 log_bin=mysql-bin binlog_format=ROW binlog_row_image=FULLVerification: Confirm binary logging is enabled:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin'; SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format';The results should show:
log_bin: ON
binlog_format: ROW
User Privileges: The MySQL user needs specific permissions:
GRANT SELECT, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'unify_reader'@'%'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;CONNECTION PERMISSIONS
-- Create user and allow connection to the MySQL server CREATE USER 'etl_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPassword!2024'; -- Grant connection access to a specific database GRANT USAGE ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%';READ PERMISSIONS
-- Allow reading data from tables and views GRANT SELECT ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Allow reading view definitions (optional) GRANT SHOW VIEW ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%';WRITE PERMISSIONS
-- Allow inserting data into tables GRANT INSERT ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Allow updating existing data GRANT UPDATE ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Allow deleting records GRANT DELETE ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%';EXECUTION PERMISSIONS
-- Allow executing stored procedures and functions GRANT EXECUTE ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%';CREATE PERMISSIONS
-- Allow creation of new tables, views, procedures, functions GRANT CREATE ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Allow creating temporary tables (optional, often needed in ETL) GRANT CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%';ALTER AND DELETE PERMISSIONS
-- Allow altering tables (add/drop columns, modify data types) GRANT ALTER ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Allow dropping tables, views, procedures, etc. GRANT DROP ON your_database_name.* TO 'etl_user'@'%'; -- Grant global RELOAD privilege (required for some replication, metadata, or flush operations) GRANT RELOAD ON *.* TO 'connector_user'@'%';Binary Log Retention: Set appropriate retention period:
SET GLOBAL binlog_expire_logs_seconds = 604800; -- 7 days
CRUD Operations Tracking
All database operations from MySQL sources are identified and logged as unique actions:
| Operation | Description | Business Value |
Create | New record insertions | Track new product listings or customer registrations |
Read | Data retrieval actions | Monitor query patterns and data access |
Update | Record modifications | Audit changes to product prices or inventory levels |
Delete | Record removals | Compliance tracking for order cancellations |
This comprehensive logging supports audit requirements and troubleshooting efforts.
Supported Data Types
| Category | Supported Types |
Integer | TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, BIGINT |
Decimal | NUMERIC, FLOAT, DOUBLE, DECIMAL |
Date/Time | DATE, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, TIME |
String | CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT |
Binary | BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB |
Boolean | BOOLEAN (alias for TINYINT(1)) |
Bit-field | BIT |
All common MySQL data types are supported, enabling comprehensive data extraction from various MySQL applications.
Prerequisites and Permissions
To establish a successful MySQL source connection, ensure:
Access to an active MySQL Server instance (version 5.6 or later recommended)
Minimum required permissions: SELECT, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT
Binary logging enabled for change data capture
Proper network connectivity and firewall rules allowing access on MySQL port
Common Business Scenarios
E-commerce Data Integration
Extract product, inventory, and order data from MySQL databases
Configure real-time order status updates
Ensure proper tracking of inventory changes
Web Analytics Consolidation
Connect to MySQL databases storing web analytics data
Optimize extraction for high-volume user behavior tables
Configure appropriate sampling for very large datasets
Customer Management
Extract customer profiles and activity data
Ensure proper handling of personally identifiable information (PII)
Implement data masking or filtering as needed for compliance
Best Practices
| Category | Recommendations |
Performance | Create read replicas for heavy extraction workloads Extract only necessary columns to minimize network load Use WHERE clauses with indexed columns to filter large tables |
Security | Create dedicated MySQL users with minimum permissions Use SSL/TLS encryption for data in transit Implement network-level security with firewalls and VPCs |
Data Governance | Document source-to-target mappings Maintain data lineage for compliance reporting Set up alerts for binary log purging or pipeline failures |
Optimization | Configure appropriate binary log retention periods Index frequently queried columns in source tables Use InnoDB storage engine for transactional consistency |
By properly configuring your MySQL source connections and following these guidelines, you can ensure reliable, efficient data extraction while meeting your business requirements for data timeliness, completeness, and compliance.