Overview
The condition node enables conditional logic within the automation, allowing automations to branch based on specified criteria, similar to an if-else statement in programming.
Users can define conditions that, when met, triggers action in the "yes" branch, while alternative actions can be initiated from the "no" branch if the conditions are not met.
.png&w=1080&q=75)
.png)

Note
By default, each branch of the condition node contains a blank node. These can be deleted if necessary, but at least one branch must contain a node.
Operations Supported
The condition node allows you to perform the following conditional operations:
| Operators | Description |
Equals to | Checks if the field value is exactly equal to the specified value. |
Does not equal | Checks if the field value is not equal to the specified value. |
Contains | Checks if the field value contains the specified substring. |
Does not contain | Checks if the field value does not contain the specified substring. |
Match Regex | Checks if the field value matches the specified regular expression pattern. |
Does not match regex | Checks if the field value does not match the specified regular expression pattern. |
Starts with | Checks if the field value begins with the specified substring. |
Ends with | Checks if the field value ends with the specified substring. |
Less than | Checks if the field value is less than the specified value. |
Less than or equal to | Checks if the field value is less than or equal to the specified value. |
Greater than | Checks if the field value is greater than the specified value. |
Greater than or equal to | Checks if the field value is greater than or equal to the specified value. |
Is present | Checks if the field value is present (not null or empty). |
Is not present | Checks if the field value is not present (null or empty). |
Use Case
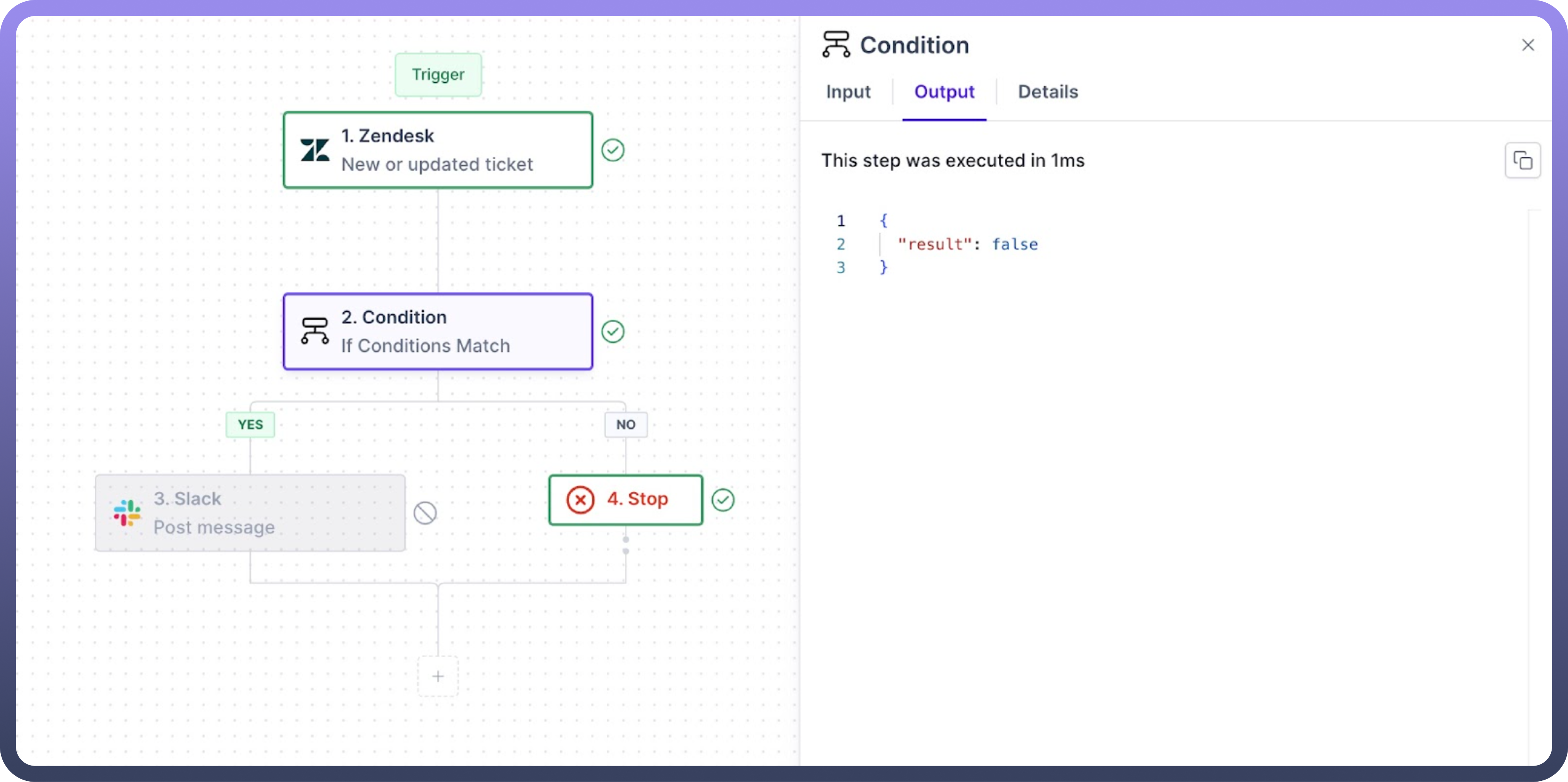
Let's take an example of how you can get notified via Slack for all the high-priority tickets in Zendesk.
Here, we receive ticket details from Zendesk whenever any new ticket is created, or an existing ticket is updated.
.png&w=1080&q=75)
.png)
Set a condition on the node where the '
priority' field is compared using the 'equals to' operator with 'high' to filter out the high-priority tickets.Select '
Slack' as the app in theyesbranch of the condition node. Then, choose 'Post Message' as the action for the app to send a message.In the
nobranch of the condition node, choose the 'stop' node to terminate the conditional flow when ticket priority is not high.
Input Features
Flexible Conditions: Define criteria based on text, numbers, dates, boolean values, and other data types.
Conditional Operators: When grouping two conditions, use
ANDto require both conditions for a true result, or useORto require only one condition for a true result.Grouping: Use the group button to combine multiple conditions, condition groups are useful when you want to implement a complex logic including both OR and AND .
For Example , When a ticket is created in Zendesk, if the ticket priority is “
High” and status of the ticket is either “Open” or “Awaiting Assignment”, then send an email to the support team.
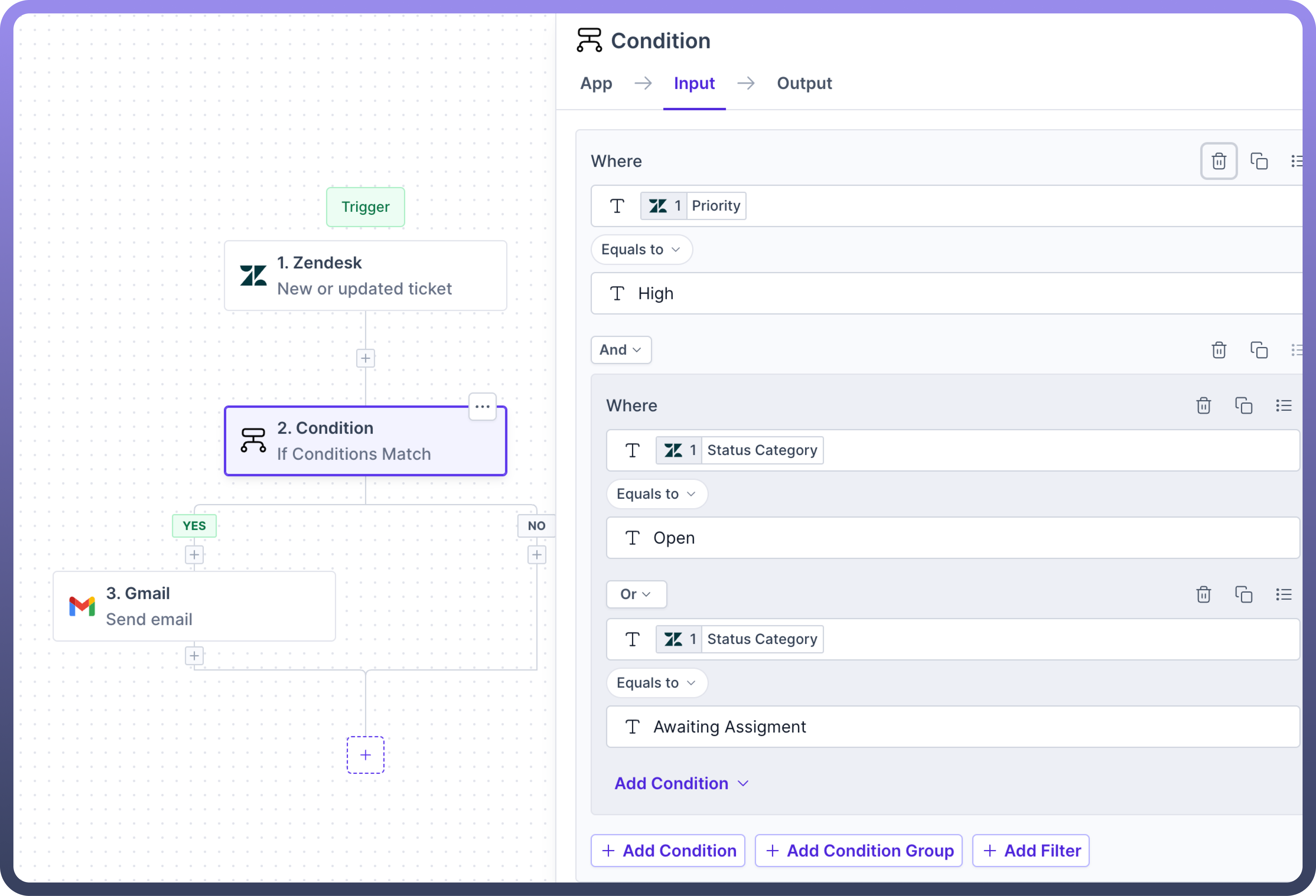
In the above scenario, the condition for the ticket's status being either "
Open" or "Awaiting Assignment" will be grouped with "OR" operator, while the requirement for the ticket priority to be "High" will be grouped alongside the status condition using “AND” operator.
Deletion: Use the
deletebutton to delete any condition or group of conditions directly.Cloning: Use the
clonebutton to duplicate any condition or group of conditions without manually re-entering them.Filtering: Filtering for specific variables can be added to the condition node to provide filtered results to the node.
Nested Conditions: Create hierarchies of conditions within nodes to handle diverse automation scenarios effectively.
Output Parameters
The output of a condition node is specified as a boolean parameter, resulting in either true or false. These outcomes determine the execution paths for the yes and no branches of the node, respectively.